why hyperkalemia in dka Episode 29 – hyperglycemia
Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic Coma - two potentially life-threatening conditions that can arise in patients with diabetes. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for these conditions is crucial for healthcare professionals working with diabetic patients. Additionally, Hyperkalemia, characterized by high levels of potassium in the blood, is another condition that requires close attention and proactive management. In this post, we will explore these three topics in detail, providing valuable insights for medical professionals.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a severe complication that can occur in individuals with diabetes, typically those with type 1 diabetes. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, the presence of ketones in the urine, and a metabolic imbalance. This condition typically arises due to insufficient insulin levels, leading to the breakdown of fats instead of glucose for energy.
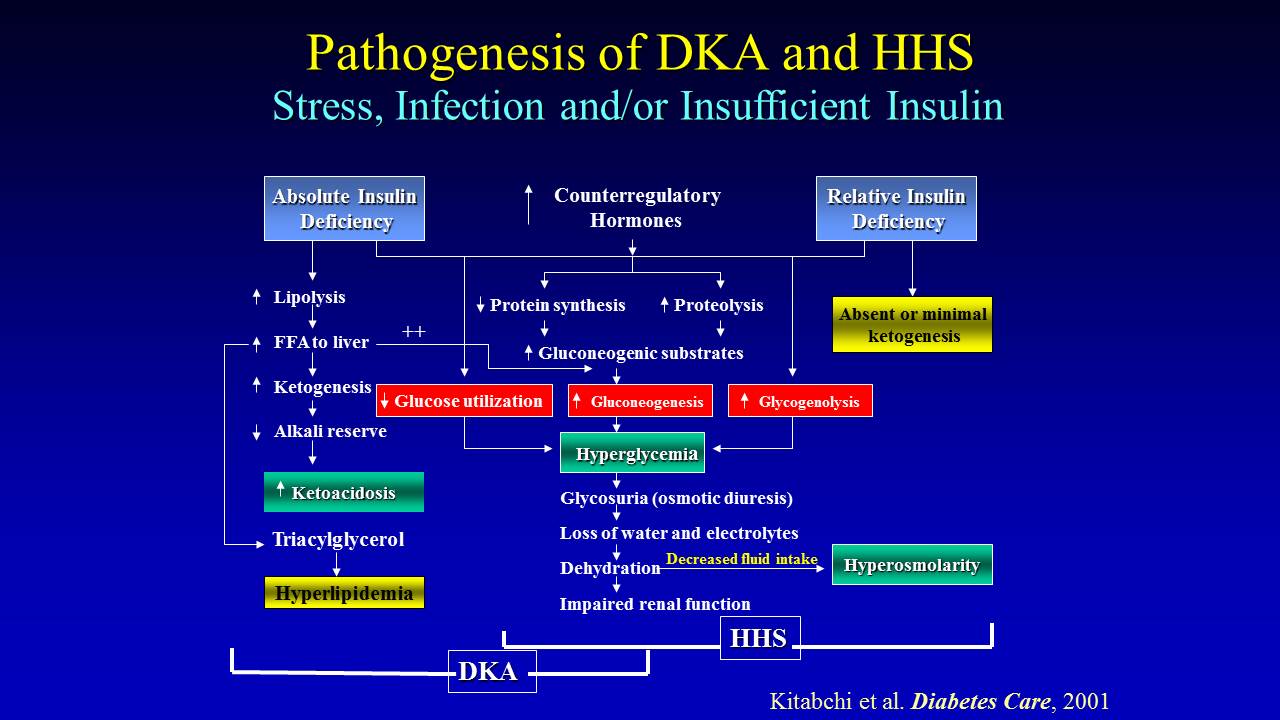 Patients with DKA often experience symptoms such as extreme thirst, frequent urination, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Left untreated, DKA can progress rapidly and lead to a diabetic coma, a life-threatening situation. Timely intervention with intravenous fluids and insulin administration is crucial to prevent further deterioration in the patient’s condition.
Patients with DKA often experience symptoms such as extreme thirst, frequent urination, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Left untreated, DKA can progress rapidly and lead to a diabetic coma, a life-threatening situation. Timely intervention with intravenous fluids and insulin administration is crucial to prevent further deterioration in the patient’s condition.
Hypersmolar Non-ketotic Coma
Hypersmolar Non-ketotic Coma (HNC) is another serious complication associated with diabetes, typically observed in elderly individuals with type 2 diabetes. Unlike DKA, HNC is characterized by extremely high blood sugar levels without the presence of ketones in the urine. This condition usually arises due to a combination of factors such as severe dehydration, underlying infections, and certain medications.
 Individuals with HNC often present with symptoms such as extreme thirst, dry mouth, confusion, weakness, and seizures. If left untreated, HNC can also lead to a coma and potentially be fatal. Treatment involves prompt administration of intravenous fluids, correction of electrolyte imbalances, and close monitoring of blood glucose levels.
Individuals with HNC often present with symptoms such as extreme thirst, dry mouth, confusion, weakness, and seizures. If left untreated, HNC can also lead to a coma and potentially be fatal. Treatment involves prompt administration of intravenous fluids, correction of electrolyte imbalances, and close monitoring of blood glucose levels.
Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia refers to elevated levels of potassium in the blood, which can be a serious concern for patients with various medical conditions, including diabetes. Functioning as an electrolyte, potassium plays a critical role in maintaining proper nerve and muscle function. However, excess potassium can disrupt the normal electrical activity of the heart, leading to potentially life-threatening arrhythmias.
 Patients with hyperkalemia may exhibit symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, palpitations, and irregular heartbeat. Given the potential for serious cardiac complications, healthcare professionals must closely monitor potassium levels in their diabetic patients. Treatment options include dietary modifications to restrict potassium intake, medications to enhance potassium elimination through the kidneys, and emergency measures like intravenous calcium administration.
Patients with hyperkalemia may exhibit symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, palpitations, and irregular heartbeat. Given the potential for serious cardiac complications, healthcare professionals must closely monitor potassium levels in their diabetic patients. Treatment options include dietary modifications to restrict potassium intake, medications to enhance potassium elimination through the kidneys, and emergency measures like intravenous calcium administration.
In conclusion, healthcare professionals need to be well-versed in recognizing and managing complications associated with diabetes. Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Hypersmolar Non-ketotic Coma, and Hyperkalemia pose significant risks to the well-being of diabetic patients. Timely intervention, including fluid replacement, insulin administration, electrolyte correction, and close monitoring, can make a substantial difference in patient outcomes. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and provide the best possible care to your diabetic patients.
If you are searching about Hyperkalemia, Levels and ECG Changes you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Images about Hyperkalemia, Levels and ECG Changes like Episode 29 – Hyperglycemia | FOAMcast, Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic coma - The Clinical and also Episode 29 – Hyperglycemia | FOAMcast. Here it is:
Hyperkalemia, Levels And ECG Changes
 doctoryg.blogspot.comhyperkalemia ecg changes levels treatment guidelines potassium wave stop adult electrocardiographic
doctoryg.blogspot.comhyperkalemia ecg changes levels treatment guidelines potassium wave stop adult electrocardiographic
Hyperkalemia.jpg: NUR102 _04939_FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING
bscc.instructure.comhyperkalemia
A Guide To Hyperkalemia - Stepwards
 www.stepwards.comhyperkalemia causes treatment potassium renal common symptoms stepwards signs guide excretion most
www.stepwards.comhyperkalemia causes treatment potassium renal common symptoms stepwards signs guide excretion most
Diabetic Ketoacidosis And Hypersmolar Non-ketotic Coma - The Clinical
 www.clinicaladvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic coma non ketotic dka hhs pathogenesis clinical metabolism
www.clinicaladvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic coma non ketotic dka hhs pathogenesis clinical metabolism
Episode 29 – Hyperglycemia | FOAMcast
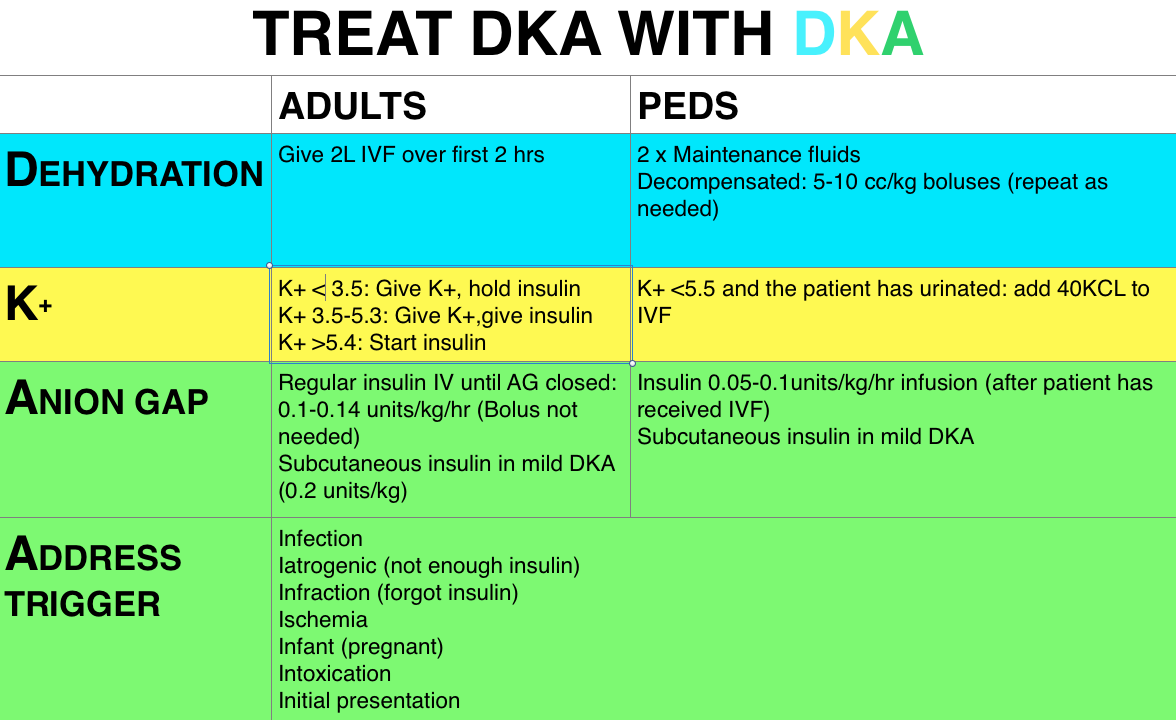 foamcast.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka hyperglycemia foamcast hyperosmolar hhs hyperglycemic insulin endocrine pediatric
foamcast.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka hyperglycemia foamcast hyperosmolar hhs hyperglycemic insulin endocrine pediatric
A guide to hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia.jpg: nur102 _04939_fundamentals of nursing. Ketoacidosis diabetic coma non ketotic dka hhs pathogenesis clinical metabolism